Control Frameworks
Why Adopting a Framework is Critical to a Robust Cybersecurity Program in Healthcare

The growing threat landscape in healthcare and why a framework is essential
The healthcare industry has always been a prime target for cybercriminals due to the sensitive and valuable nature of its data. Information such as patient health records, billing information, intellectual property, and personally identifiable information (PII) have historically represented a goldmine for cyber attackers. Recently, however, the rise of new technologies and tools that are designed to enhance care delivery, such as telemedicine, electronic health records (EHR), medical Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and artificial intelligence (AI), has also expanded the attack surface, creating more entry points for cyber threats. As a result, healthcare organizations are facing a new era of cyber risks that demands a more strategic, comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
The increasing complexity of healthcare IT systems
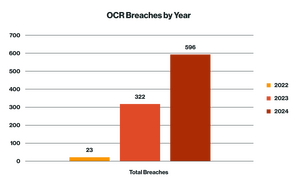
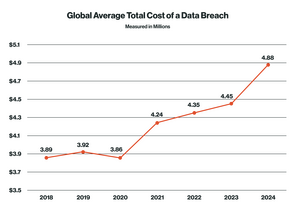
Healthcare IT systems have become increasingly complex in recent years. Providers are adopting cloud-based services, integrating EHR systems, and utilizing more connected devices, many of which were designed for convenience rather than security. Healthcare is now one of the most targeted sectors for cyberattacks, surpassing even financial institutions in terms of the volume and severity of breaches, with 2024 settings records in the number of reportable breaches. According to a report from the Ponemon Institute, 88 percent of the healthcare organizations surveyed experienced at least one cyberattack in the past 12 months with, according to a CSO report, the average cost of a breach reaching $4.8 million.
The advent of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have also introduced new vulnerabilities. For example, AI‑powered diagnostic tools require massive datasets to train models, and these datasets often include sensitive protected health information (PHI). The risk is clear: if attackers gain access to these AI systems, they can steal, manipulate, or even destroy valuable data.
Why HIPAA is no longer enough
For many years, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)’s Security Rule (45 CFR Part 160 and Subparts A and C of Part 164), currently being enhanced by legislation, has been the “de facto” standard for safeguarding patient data in the United States. The rule requires healthcare organizations to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic PHI. However, while HIPAA compliance is still a must, it does not necessarily offer a comprehensive solution for the full spectrum of cyber threats that healthcare organizations face today.
Currently, HIPAA regulations mainly address privacy and confidentiality but do not offer detailed guidelines for tackling emerging risks such as ransomware, advanced persistent threats (APTs), or insider threats. As the threat landscape has evolved, relying solely on HIPAA has proven inadequate for the complex and multifaceted nature of modern cyberattacks. Today, healthcare organizations need a more robust cybersecurity approach that goes beyond mere compliance and builds a solid foundation for long-term data protection.
The role of cybersecurity frameworks
This is where cybersecurity frameworks can be of use. Frameworks are structured sets of standards, best practices, and guidelines that help organizations manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks. They offer a proactive, systematic approach to security, which is essential for dealing with the rising tide of cyber threats in healthcare.
Cybersecurity frameworks like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Health Information Trust Alliance Cybersecurity Framework (HITRUST CSF), and International Organization for Standardization ISO 27001, can provide healthcare organizations with clear guidelines on how to safeguard patient data, secure IT systems, and develop comprehensive risk management strategies. These frameworks offer a more dynamic approach to risk mitigation than do compliance requirements that evolves as new threats emerge.
For example, NIST offers several different frameworks (NIST 800-30, 37, 39, 53, and CSF). These options can provide healthcare organizations with an appropriate roadmap for managing cybersecurity risks across the entire life cycle, from identifying potential threats to responding to breaches and recovering from incidents.
Key benefits of adopting a cybersecurity framework in healthcare
Cybersecurity in healthcare is not just about protecting patient data; it is about ensuring that the entire healthcare ecosystem, from doctors and nurses to hospitals, insurers, and patients, remains safe and functional. The rapid adoption of digital technologies and interconnected devices has significantly expanded the scope of cybersecurity threats. As a result, healthcare organizations must go beyond a HIPAA compliance framework and implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures that offer structured, multi-layered approaches to safeguarding sensitive information. Employing such frameworks can lead to enhanced risk management, streamlined compliance, structured incident response and recovery, the building of a cybersecurity culture that can help prevent events, and improved patient trust.
Enhanced risk management
One of the primary benefits of adopting a cybersecurity framework is improved risk management. A cybersecurity framework provides organizations with a structured methodology to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. NIST 800-37 Risk Management Framework (RMF), for example, emphasizes risk management as its foundation. The framework helps organizations gain a clear understanding of their assets, systems, and vulnerabilities. By conducting risk assessments and regular vulnerability scans, healthcare organizations can prioritize their risk management efforts around the most critical threats.
This proactive risk management approach helps reduce the likelihood of cyber incidents and ensures that healthcare organizations can both prevent threat exploitation and quickly respond to emerging threats. For example, if a new ransomware variant emerges, an organization with a cybersecurity framework in place will already have processes for detecting, containing, and recovering from the attack.
Streamlined compliance
Navigating the complex regulatory environment of healthcare can be challenging given that healthcare organizations must comply with a wide range of standards and regulations, including HIPAA, California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and state‑specific data protection laws. A cybersecurity framework can simplify compliance by aligning its best practices with these regulatory requirements.
For instance, NIST provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks while meeting compliance obligations across multiple standards, including HIPAA and NIST’s own cybersecurity standards. By implementing a NIST framework, healthcare organizations can streamline their compliance efforts, ensuring they address regulatory mandates efficiently while simultaneously strengthening their security posture. The framework’s comprehensive, risk-based approach offers a solid foundation for maintaining ongoing compliance and provides transparency to regulators, patients, and other stakeholders regarding the organization’s commitment to safeguarding sensitive data.
Incident response and recovery
Cybersecurity breaches are inevitable, but how an organization responds can determine their ultimate cost and impact. Cybersecurity frameworks can provide healthcare organizations with structured incident response and recovery plans that enable them to react swiftly and minimize damage. The Respond and Recover functions of frameworks like NIST CSF outline the necessary steps for handling cyber incidents, including containment, communication, root cause analysis, and recovery procedures.
The having an effective incident response plan is key to mitigating the impacts of a cyberattack. In healthcare, a data breach or system outage can delay treatment, compromise patient care, and have severe financial implications. A well‑developed response plan can help healthcare organizations to quickly recover from disruptions and to continue providing high-quality patient care.
Improved patient trust
Trust is the cornerstone of any healthcare organization. Patients expect their PHI and PII to be protected and handled with the utmost care, but they also expect continuity of care and access to services, even in the face of potential cyber threats. A robust cybersecurity framework helps healthcare organizations achieve both: securing patient data and ensuring that essential services remain available.
When systems like electronic medical records (EMRs) are targeted by ransomware or other cyberattacks, it can severely disrupt patient care. By implementing proven cybersecurity practices and incident response protocols, healthcare organizations demonstrate their commitment to protecting both patient data and the continuity of care. This proactive approach strengthens patient confidence, knowing that their health and their personal information are well protected, no matter what challenges may arise.
Building a culture of cybersecurity
Employees represent a significant vulnerability for organizations when it comes to cyberattacks. According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report: For the second consecutive year, phishing and stolen or compromised credentials were the most common attack vectors, accounting for 15% and 16% of breaches, respectively, and ranking among the top four costliest incident types, with compromised credential breaches averaging $4.81 million and phishing attacks costing $4.88 million.
Frameworks help mitigate these risks by promoting cybersecurity education and best practices at all levels of the organization. Adopting a cybersecurity framework can also foster a culture of security within an organization. Frameworks like NIST 800-53 and ISO 27001 emphasize the importance of employee training, awareness programs, and the continuous monitoring of internal processes. By integrating cybersecurity into daily workflows and emphasizing the importance of data protection, organizations can reduce the likelihood of security lapses caused by human error. Moreover, when leadership sets the tone for cybersecurity and allocates the necessary resources, employees are more likely to take data protection seriously and follow best practices.
Connect 1:1 with a Healthcare GRC Expert
