Cyber Risk Advisory
NIST Responds to the AI Executive Order with 5 New Publications

The US Executive Order (EO) on Safe, Secure and Trustworthy Development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) was released 6 months ago to enhance the safety, security, and trustworthiness of AI systems. Within the EO, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) was tasked with creating guidelines and best practices to promote industry standards for developing secure and transparent AI systems.
NIST announced their delivery of their promise and published new guidance to support the NIST AI Risk Management Framework for generative AI. These publications provide supplemental guidance on developing risk profiles, integrating AI into secure development practices, testing AI models, and planning global engagement on AI standards.
Using the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) as a baseline, organizations can enhance their ability to govern, map, measure, and manage AI risks by leveraging the additional documentation recently provided by NIST. Coalfire has analyzed these companion resources and has provided insights on the key elements below.
1. Managing Misuse Risk for Dual-Use Foundation Models
The NIST AI 800-1 Managing Misuse Risk for Dual-Use Foundation Models from the U.S. AI Safety Institute is intended to help AI Risk practitioners evaluate and mitigate the risks stemming from AI models that could be modified or used in a high-performance manner to pose a significant threat to the health and public safety of individuals. Examples include utilizing the model to facilitate the development of nuclear weapons, offensive cybersecurity attacks, non-consensual intimate imagery of real individuals, etc.
Determining the potential risk and impact of an AI model is challenging. Foundation models trained on diverse data can be applied in various ways, making it difficult to anticipate misuse. Additionally, profiling threats may require outside expertise due to the unique nature of the threat actor and their resources.
NIST AI 800-1 breaks down the threat profiling into seven steps:
- Anticipate potential misuse risk
- Establish plans for managing misuse risk
- Manage the risks of model theft
- Measure misuse risk
- Ensure that misuse risk is managed before deploying foundation models
- Collect and respond to information about misuse after deployment
- Provide appropriate transparency about misuse risk
Following NIST’s guidance here will assist the organization with the ability to govern, map, measure, and manage their AI risks, in accordance with their AI Risk program. While these tasks align to the majority of the practices within NIST AI RMF, a few specific subcategories include:

2. Generative AI Risk Profiling
The NIST AI 600-1 AI RMF Generative AI Profile is a companion resource to the NIST AI RMF. This publication provides details on specific risks that are unique or exacerbated by generative AI. The publication defines 12 unique risks organizations can frame and execute risk management efforts. These risks include:
- Chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear (CBRN) Information or Capabilities
- Confabulation
- Dangerous, Violent, or Hateful Content
- Data Privacy
- Environmental Impact
- Harmful Bias or Homogenization
- Human-AI Configuration
- Information Integrity
- Information Security
- Intellectual Property
- Obscene, Degrading, and/or Abusive Content
- Value Chain and Component Integration
Organizations can leverage the NIST AI 800-1 for guidance on conducting a risk/impact analysis, with the 12 factors in NIST AI 600-1 to develop comprehensive AI risk profile(s) of their AI model(s). This publication also provides suggested actions for responding to risks. To help further streamline efforts, these actions/risks are mapped to the NIST AI RMF.
For example, let’s say that the organization deems a risk of harmful bias in their Generative AI model. NIST defines harmful bias as the amplification of historical, societal, and systemic biases, incorrect presumptions of performance (possibly due to non-representation in training data), which may result in discrimination, erroneous outputs, and ill-founded decision-making. If this is a potential risk within your model, the NIST publication suggests some of the following:

3. Secure Software Development Practices for Generative AI
The NIST SP 800-218A: Secure Software Development Practices for Generative AI and Dual-Use Foundations Models adds practices, recommendations, considerations, and informative references specific to artificial intelligence (AI) model development throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC).
As part of Coalfire’s advisory and assessment work in the AI risk space, one of the most common programmatic gaps we have identified is the lack of security-by-design within AI model development. The NIST SP 800-218A framework can guide an organization to integrate into the current SDLC. One limitation to note is that this framework is strictly for integrating information security into the SDLC and does not address the additional AI risks, such as harmful bias, data privacy, as noted in NIST AI 600-1.
The NIST SP 800-218A framework specific lays out each element of an SDLC program and how to layer on AI considerations. In the example below, the framework provides guidance on incorporating AI digital signatures as part of software integrity mechanisms. See the excerpt from the framework below:

By integrating AI into the SDLC, developers can meet several NIST AI RMF best practices. Specific subcategories include, but are not limited to:

4. Test Software for the Characterization of AI Technologies
Any comprehensive SDLC program must include technical testing of software. Dioptra provides an open-source testing platform designed to help AI system users and developers measure how certain types of attacks can degrade the performance or trustworthiness of an AI system. Trustworthy tests include ensuring the AI model is valid and reliable, safe, secure and resilient, accountable and transparent, explainable and interpretable, privacy-enhanced, and fair. AI models can be tested through the development lifecycle (1st party testing), during acquisition (2nd party testing), or as part of auditing or compliance (3rd party testing).
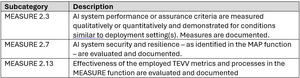
By testing how AI system models respond to attacks, developers can meet the Measure function of the NIST AI RMF. Specific subcategories include, but are not limited to:
5. Plan for Global Engagement on AI Standards
The NIST AI 100-5 A Plan for Global Engagement on AI Standards proposes a plan for US stakeholders to work with others around the globe on AI standards. Globally, AI regulations have sharply increased. Last year alone, the total number of AI-related regulations enacted in the US grew by 56.3%. As part of Coalfire’s advisory and assessment engagements, we have learned that many organizations are frustrated by the lack of continuity between global frameworks and regulations and are hesitant to commit to a framework with the expectation that new regulations could arise. NIST plans to address these concerns through an open, transparent, and consensus-driven process.
A few of the US government’s high-priority implementation actions:
- Identify and allocate dedicated AI resources, including dedicated R&D funding
- Consult with private sector organizations on AI standards. Convene on periodic knowledge sharing meetings
- Share priorities and views on AI standards development and adoption between agencies in order to increase agency participation and adoption
- Work on standards development projects jointly with governments around the world. Build discussion protocols in order to work with key allies and countries to align on shared principles for AI standards
- Translate key US government documents, AI standards, and related resources into multiple languages
While this publication is a declaration of activities by the US government, it is essential for organizations to keep up to date on national and global AI standards and regulations, to maintain a functional AI Risk program. Related subcategories within the NIST AI RMF include, but are not limited to:

Coalfire has assisted organizations across multiple industries to understand their unique AI, cybersecurity, and privacy risks. Reach out to info@coalfire.com for additional information on our AI Risk Services.