Risk-Analysis
Cost of OCR Investigations
Analyzing the cost per record of healthcare data breaches

Data breaches have emerged as a prevalent threat in today’s interconnected digital environment, impacting organizations across various sectors. However, the healthcare industry is particularly vulnerable, facing greater financial repercussions per compromised record.
As healthcare organizations increasingly digitize records to enhance patient care and streamline operations, they inadvertently expose themselves to substantial cybersecurity risks. According to the 2024 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, healthcare organizations represented 11% of all U.S. data breaches in 2024. Such frequency increases the importance for healthcare organizations to understand the financial implications associated with these incidents.
The value of medical records on the black market
Hackers target medical records because they are more valuable than other types of personal data, such as credit card information, which typically sells for much less. On the black market, the cost of medical records is notably high, reflecting their value to cybercriminals. According to a recent analysis by Keeper, the cost of medical records on the black market (over $1,000 each) starkly contrasts with the value of personal information from other industries. For instance, credit card details typically fetch only $5 to $20, while login credentials for online accounts may sell for $1 to $10. This staggering price difference is due to the wealth of sensitive information that medical records contain, including personal identification details, medical histories, and insurance information. The increased market value of healthcare data can also be attributed to several factors:
- Use in fraudulent activities: Stolen healthcare information is highly valuable for identity theft, filing false insurance claims, and obtaining medical services fraudulently. This propensity for misuse drives demand and, consequently, market prices.
- Scarcity of healthcare data: The unique and sensitive nature of healthcare records makes them more desirable than other data types, enhancing their market value. Criminal organizations actively seek this data to facilitate a wide range of illicit activities.
- Impact on victims: The long-term consequences of healthcare data breaches can be devastating for individuals, leading to identity theft, compromised medical care, and significant emotional distress, further amplifying the perceived value of such information on the black market.
Medical records can be used for identity theft, fraud, and various forms of financial exploitation. Further, medical record information is not only useful for immediate financial gain but can also be exploited over a longer period. As the demand for such sensitive information persists, the black market for medical records continues to thrive, posing significant risks to individuals and healthcare institutions alike.
Given the attractiveness of medical records for cybercriminals, how do healthcare organizations protect themselves? And what are the costs if they don’t?
Role of HHS
Healthcare cybersecurity regulatory frameworks: the role of the HHS
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) plays a critical role in enforcing Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 regulations. The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) within HHS is responsible for investigating complaints and conducting compliance reviews related to HIPAA violations. The OCR has the authority to impose civil monetary penalties and ensure that organizations take corrective actions following a breach.
According to the 2024 HIPAA Accomplishments and Wrap-Up by HHS, OCR was very active with HIPAA enforcement throughout 2024. OCR completed 22 HIPAA enforcement actions (the second highest in OCR history) and collected over $9.9 million in settlements and civil money penalties. Issues resolved included violations related to ransomware, phishing, health information left unsecured on the internet, impermissible access to ePHI, reproductive health information impermissibly disclosed, and untimely patient access to PHI.
Any calculation of the economic impact of data breaches within the healthcare sector must, therefore, include the financial burden of regulatory fines in combination with the costs related to the required corrective actions.
Organizational costs
Cost per record for healthcare organizations
The financial impact of a data breach for healthcare organizations is multifaceted, encompassing various key components that generally fall into the two categories of direct and indirect costs:
- Direct costs: Immediate expenses arising from a data breach include the cost of breach notifications, forensic investigations, legal fees, and regulatory fines. For instance, a healthcare provider may incur costs related to notifying affected patients, engaging cybersecurity firms to investigate the breach, and addressing any legal ramifications.
- Indirect costs: Indirect costs often surpass direct expenses and can significantly affect the long-term financial health of the organization. These costs may include reputational damage, loss of patient trust, increased insurance premiums, and potential business loss due to operational disruptions.
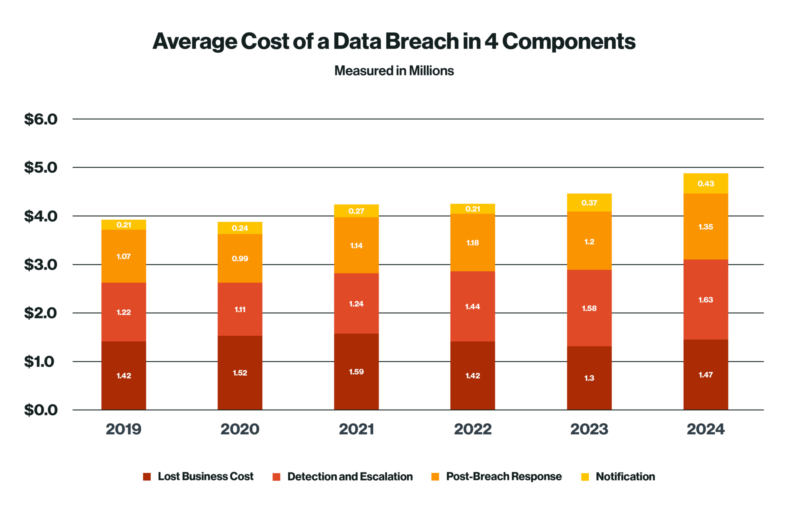
Figure 3: Total cost of a data breach - healthcare vs general by industry
- According to the 2024 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average total cost of a healthcare data breach reached approximately $9.7 million, compared to an overall average cost of $4.88 million, with an average cost per medical record escalating to $500+.
- This figure marks a notable increase over the previous year’s reported cost and remains significantly higher than the average cost per record in other industries, which stands at around $10-100+.

Figure 2: Total cost of a data breach - healthcare vs general by year
Comparison with other industries
The healthcare industry has with notably higher average costs associated with data breaches. As stated above, recent data from IBM (Figure 3) states that healthcare incurs an average cost ($9.77 million) per breach far surpassing the costs faced by other industries.
For context, the financial services sector averages around $6.08 million, while technology firms experience costs averaging $5.45 million. Other industries, including public services, retail, and education have significantly lower average costs, ranging from approximately $2.55 million to $4.09 million.

Figure 3: Total cost of a data breach - healthcare vs general by industry
This stark contrast underscores the unique vulnerabilities and regulatory challenges faced by healthcare organizations, which must safeguard highly sensitive patient information while navigating stringent compliance requirements such as HIPAA and other frameworks.
Several factors contribute to the disparity in breach costs between healthcare and other sectors:
- Regulatory compliance: Healthcare organizations are subject to stringent regulations such as HIPAA, which necessitates significant investment in security infrastructure and legal counsel, leading to higher overall costs.
- Sensitive nature of data: Healthcare records contain highly sensitive personal information, including medical histories, Social Security numbers, and insurance details. This sensitivity increases both the impact of breaches on patients and the costs associated with remediation.
- Complexity of healthcare systems: The intricate nature of healthcare systems, characterized by numerous interconnected entities and technologies, creates multiple potential points of vulnerability. This complexity complicates security efforts and raises costs.
The heightened financial impact of data breaches in healthcare not only affects organizational bottom lines but also threatens patient trust and the integrity of the healthcare system. As such, understanding these costs and the factors driving them is critical for healthcare leaders seeking to bolster their cybersecurity posture and protect their valuable data assets.
Data breach trends and projections
Ransomware is projected to escalate significantly in 2025, as attackers continue to evolve their strategies by targeting critical suppliers that entire industries depend on. The impactful 2024 attacks on CDK Global and Change Healthcare highlighted the extensive disruption caused when a single supplier is compromised, affecting automotive services and healthcare providers nationwide. As a result, there is an urgent need for comprehensive risk analysis within the healthcare industry.
Key trends include:
- Increased ransomware attacks: Ransomware attacks on healthcare organizations have risen sharply, indicating that 67% of healthcare breaches involved ransomware in 2024, a significant increase from previous year of 60%, according to Sophos. These attacks not only disrupt operations but also drives up costs as organizations must address the immediate threat while also managing the fallout.
- Greater regulatory scrutiny: As data breaches continue to rise, regulators are likely to impose stricter compliance measures on healthcare organizations. The potential for increased fines and sanctions will further elevate the costs associated with data breaches.
Action steps for mitigating the risk of breaches
To mitigate the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations, Coalfire recommends that healthcare organizations implement the following administrative, physical, and technical safeguards:
Administrative safeguards
- Risk assessment: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement in the organization’s data protection practices.
- Training and awareness: Provide comprehensive training for employees on HIPAA compliance, data privacy, and security protocols. Regular training updates can reinforce the importance of safeguarding PHI.
- Policies and procedures: Develop and maintain clear policies and procedures regarding the handling of PHI. Ensure these are communicated effectively to all staff.
- Incident response plan: Establish and regularly test an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach, ensuring that all employees know their roles and responsibilities.
Physical safeguards
- Access controls: Implement physical access controls to restrict unauthorized personnel from entering areas where PHI is stored or processed. This may include locked doors, security badges, and visitor logs.
- Secure storage: Ensure that physical records are stored securely, such as in locked cabinets or rooms. For electronic devices containing PHI, use secure locations to minimize risk.
- Device management: Maintain a policy for the secure disposal of old hardware and electronic devices that may contain PHI, ensuring that data is irretrievably erased before disposal.
Technical safeguards
- Data encryption: Use encryption for ePHI both in transit and at rest to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Access controls: Implement strong access control measures, such as unique user IDs, passwords, and multi‑factor authentication, to limit access to sensitive data.
- Regular audits: Conduct regular audits of information systems to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations and to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Patch management: Keep software and systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
The cost per record for healthcare data breaches remains markedly higher than in other industries, driven by both organizational costs and the substantial black-market value of stolen information. As healthcare organizations increasingly rely on digital systems to manage sensitive patient data, the risks and costs associated with data breaches are only predicted to grow. Stakeholders within the healthcare sector must prioritize investments in advanced cybersecurity measures and compliance strategies to effectively mitigate these risks.
By implementing comprehensive administrative, physical, and technical safeguards, healthcare organizations can enhance their compliance with HIPAA and significantly reduce the likelihood of data breaches. Understanding the financial implications of data breaches and the evolving landscape of cyber threats is crucial for healthcare organizations to better prepare for and respond to potential breaches. Enhanced compliance with HIPAA and proactive engagement with HHS can further protect organizations against the financial and reputational damage associated with data breaches, ultimately safeguarding the welfare of patients.
Next Steps
- Conducting an OCR-9 Risk Analysis
- Contact Us for more information on Risk Analysis.
Connect 1:1 with an OCR Expert
